What is blockchain: blockchain technology

In recent months, the cryptocurrencies, NFTs and metaverses has been booming. We have heard news both on television and on social networks.
It seems that these new technologies are here to stay and that they will be the future of currencies, art or social interactions.
What do all these concepts have in common? All these technologies are based on a very particular term: the blockchain or the blockchain.
In this article we will give an extended introduction to what blockchain is, how it works and what projects and applications use this technology.
Stay and learn once and for all what the hell this blockchain thing is!
How blockchain technology works
The blockchain is based on two very basic principles: decentralization and consensus . The objective of this methodology is to achieve a secure, distributed and efficient method of storing data so that no one can manipulate it.
Let's look at it in more detail.
Decentralized systems
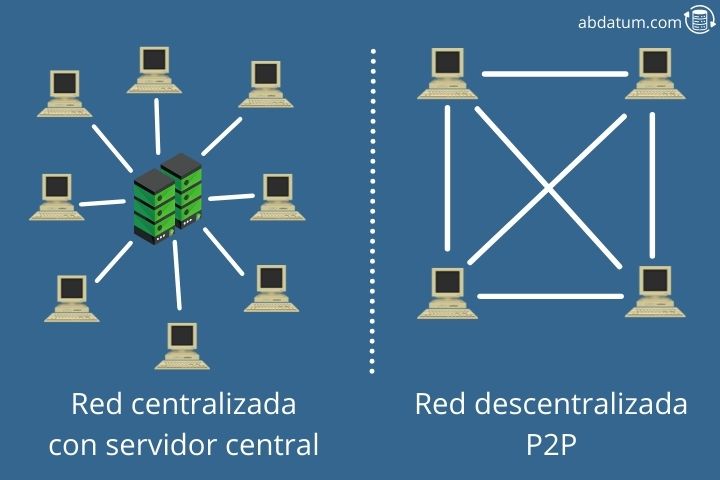
A very important point of this technology is decentralization. Nowadays, most information is stored on servers of large private institutions.
For example, we have all our money in banks, which are still a centralized system controlled by a single multi-billion dollar company.
Thanks to the blockchain we get democratize all this information . The data no longer depends on a central company but is distributed within a network and is controlled by the network participants themselves. These participants are called network nodes.
Let's take an example. We all know bitcoin. Bitcoin is a cryptocurrency that is based on blockchain technology. In this case they are the nodes of the network themselves, that is, you, me and the rest of the people like us who have their money in bitcoin.
In this way, we are not controlled by large financial companies, but rather the bitcoin network itself that regulates itself thanks to its participants.
Do you realize the advantages that this entails? It is no longer the banks that decide about our finances.
Networks Peer-to-Peer (P2P)
Decentralized systems make use of what is known as Peer-to-Peer (P2P) . This is not new. Do you remember when we used Emule to download movies or music?
These files were not on a central server, but were the Emule users themselves who had the different files and we downloaded those movies that other users had.
Blockchain technology works the same. We continue with the example of bitcoin (later we will see many more applications).
A currency system basically works by recording all transactions that occur with that currency. Bitcoin works the same. All participating nodes are listening to the transactions taking place and recording them.
Being a P2P network, if any of the nodes fails the system continues to function since there are many others working.
All transactions are updated by the nodes themselves. But there is a problem. How do we order these operations?
Each node has its own internal computer time. So we cannot know which transaction has occurred before. We could try to synchronize all the computers, but it would be a very complex problem.
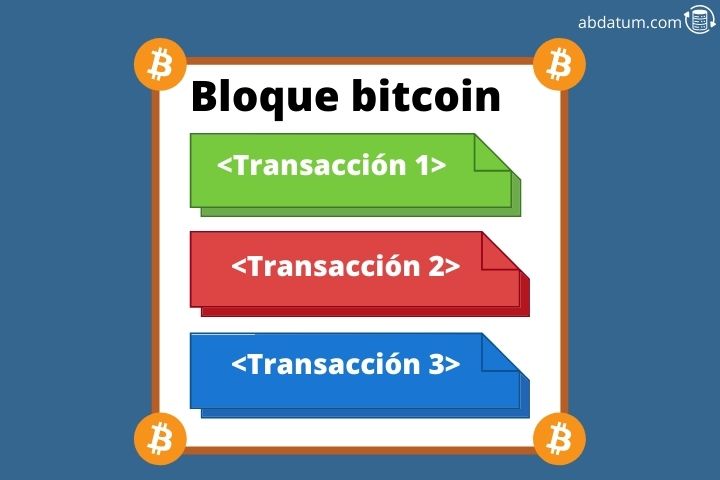
What is a block?
The blockchain solution consists of creating what we know as blocks. That is to say, we group the transactions that have occurred in a given window of time in a block of information.
Therefore, the work of the different nodes of the network would be listen to transactions that occur and group them into blocks . In addition, they also have to validate said operation by verifying that it can happen.
Now all that remains is to decide which block we consider valid since all participants in the bitcoin network are listening and creating blocks for the same transactions.
We could use some voting system to choose the final block. However, this could pose a security problem.
The same computer could participate in the vote several times, posing as different nodes using virtual IPs. This is known as Sybil Attack . How do we solve this security problem?
Work test ( Proof of Work )
The solution that was found is to pay a computational cost for adding a block of information to the network.
If a computer impersonates several computers then it will have to perform a much higher computational cost and therefore the other nodes will perform it more quickly.
This is known as proof of work or in English, proof of work (POW).
The proof of work of this type of networks consists of finding a random number that meets certain rules. Let's go deeper into this concept.
Before explaining how the POW works, it is important to explain some previous concepts about cryptography.
In cryptography we talk about a hash function as a mathematical operation that converts any type of information into a single string of values.
For example, if we take a text, this text has an associated string of numbers and letters when we pass it through the hash . Just change a comma, this string of values is already a completely different one.
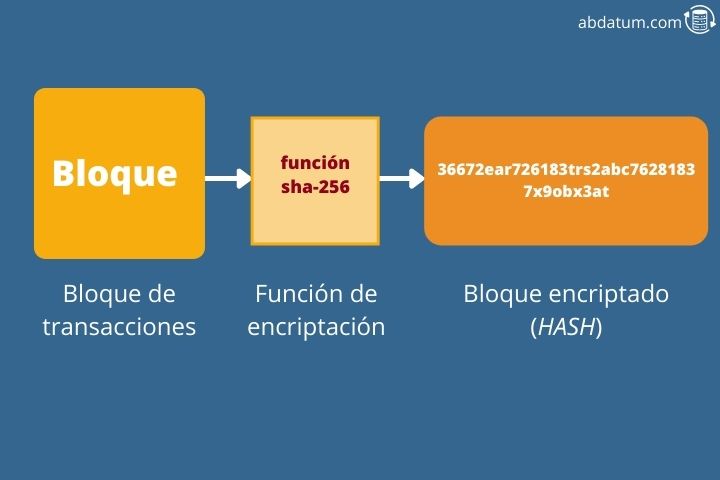
These mathematical operations are widely used in modern cryptography. Blockchain technology makes use of one of these encryption functions: the SHA-256 .
What do these operations have to do with proof of work?
The computational cost that we have mentioned uses this concept of cryptography to avoid the sybil attacks .
Once a node has a block, to add it to the main network it has to solve the following cryptographic problem:
The new block of information is transformed into a string of values called a hash through the function SHA-256 that we just explained.
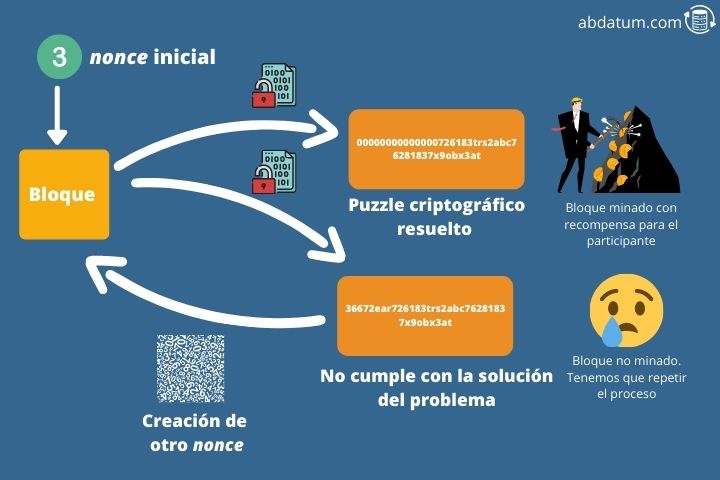
In addition to the block's own information (in the case of bitcoin, the different transactions that have occurred in a given time frame), a unique random number called nonce .
The cryptographic problem consists of finding the nonce that, together with the block information, generates a hash that begins with a certain number of zeros.
Finding this number or nonce that makes the hash start with many zeros is a really complicated problem to solve.
Block chain mining
Find the nonce and adding the block to the main chain is known as mining a block.
But why did the different nodes spend their computational power to mine these blocks of information?
Obviously for the network to work there must be some incentive for participants to want to make this computational effort.
When one of the nodes manages to solve the cryptographic puzzle and add the mined block to the main chain, then this participant is rewarded through a transaction assigned to him that gives him an amount of the cryptocurrency, in this case, bitcoin.
This has caused what are known as mining farms to be generated. Sites with a huge number of processors running 24 hours a day to be able to mine and therefore earn money by adding blocks to cryptocurrency networks.
There has been much debate as to whether this mining system is harmful to the environment. There are other alternatives to proof of work that are beginning to be applied.
One of them is the proof of stake (POS) which in the next version of Ethereum will be used as a replacement for POW. This will mean that said cryptocurrency can no longer be mined.
In another article we will talk in more depth about these new methodologies. eco friendly than proof of work.
The blockchain or blockchain
We have already seen what decentralized networks are and how mining works within blockchain technology.
We have one last question left to resolve. How do we ensure that these blocks are immutable and cannot be altered?
It turns out that in addition to the nonce and the hash of the previous block is also incorporated from the block data. This makes each block related to its previous and next block, creating the famous chain of blocks or blockchain.
If someone is able to alter any of the blocks in the chain then its hash will change and will no longer match the hash incorporated in the next block, altering the entire chain and breaking the relationships between blocks since the hashes They will no longer match.
You would need to have access to 51% of all nodes on the network to be able to break the security and modify the blocks as you please. Made impossible in most blockchains due to the enormous number of nodes that these networks incorporate.

Applications of blockchain technology
To explain and so that you can understand how a blockchain works, we have used a well-known example such as bitcoin. However, this technology is applicable to an infinite number of different sectors. Let's look at some examples.
Cryptocurrencies
The first example, as it could not be otherwise, is cryptocurrencies. We have seen how bitcoin works but there are many more decentralized digital currencies that use their own blockchain such as Ethereum, BNC or Polkadot.
Non-fungible tokens (NFT)
In recent months, non-fungible tokens or NFTs have gained a lot of popularity.
Non-fungible tokens are related to digital assets such as digital art that, thanks to the blockchain, can represent something unique, guaranteeing its authenticity.
The owner of that digital asset is unique and can be verified since said information is on the blockchain (in the case of NFTs, normally on Ethereum).
This allows purchases and sales to be made as if it were physical art such as paintings or sculptures.
Smart contracts
Smart contracts or smart contracts , are contracts between two natural persons that cannot be broken since they are in the form of code within the blockchain.
For example, imagine that we design an NFT and we want to create a smart contract that says that every time our NFT is sold we get a 5% commission.
This contract is stored eternally within the blockchain. It is immutable and no one will be able to alter it, so whenever the NFT that we create is sold, we will take said commission.
Decentralized finance or DeFis
Decentralized finance seeks to replace traditional finance with a much more transparent and decentralized system.
These make use of what we saw previously, smart contracts, to be able to give loans. The conditions of said contract will be immutable and public thanks to the fact that it will be on a blockchain.
DeFis allow financial tools to no longer be controlled by banks, multi-million dollar private identities, but to be managed by the network of nodes in which all of us can participate.
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs)
DAOs are organizations that are completely controlled by smart contracts hosted on a blockchain. This allows the creation of much more transparent, self-managed and efficient organizations.
All the information of said organization would be public and everyone could access it. In addition, contracts between organizations would also be decentralized and immutable.

